Bulimia or Bulimia Nervosa is signified by compulsive overeating, and then purging (removing the food) to get rid of the calories. The person has a constant uncontrollable urge to eat, and then throw up all the food to prevent weight gain. This is a severe health condition, and can result in critical health risks.To know about the types and risk factors of builimia visit: Bulimia: Definition, Types and Risk Factors
How common is Bulimia?
Bulimia is twice likely to occur in women than in men. Studies show that 1 to 3% of adolescents; especially young women have bulimia nervosa. The disorder is more likely to occur in teenage and late twenties or thirties. Among those having bulimia, one third people have had an earlier record of Anorexia nervosa. Also, Bulimia is seen common in people having obesity or those having obese parents.
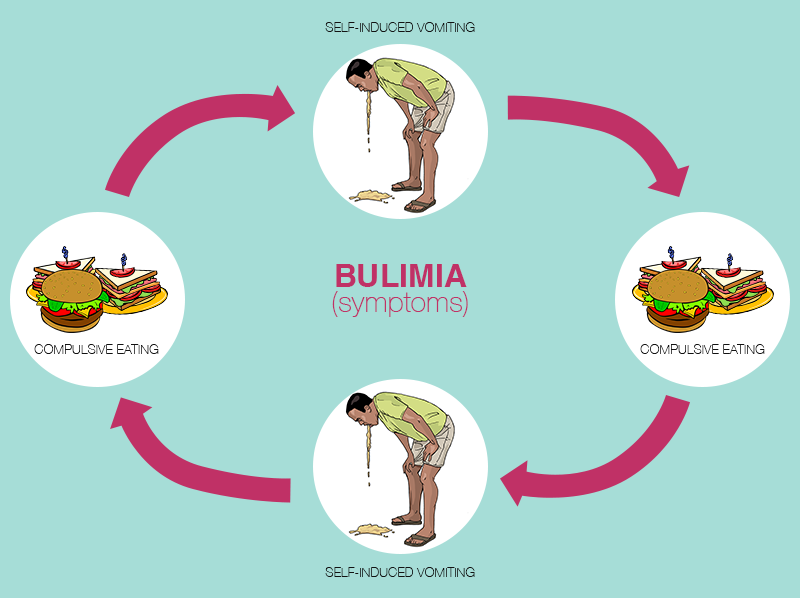
How is Bulimia a vicious cycle?
Bulimia is signified by two major parts; firstly the person eats too much to the extent of feeling sick, and then secondly he/she purges, most of the times by vomiting in order to get rid of the eaten food. Non purging bulimia is characterized by doing tough and rapid exercises to sweat away the calories. However, the disorder becomes a vicious cycle.
The elimination of food in such vigorous ways cause nutritional deficiency in the body. In response to this, the stomach will ask for more food. The hunger and appetite gets magnified. The person will have to overeat to satisfy the stomach, and immediately feel guilty of eating too much. This will lead to purging, and the purging again leads to more hunger. This becomes an unbreakable form of cycle eventually.
What Causes Bulimia?
Several factors can cause bulimia to evolve in a person such as:
Biological factors
Bulimia Nervosa can be caused by a series of biological abnormalities. Research at NIH (National Institute of Health, the U.S) showed that low levels of Peptide Cholecystokinin (a hormone in the gastrointestinal system) can cause a person to not feel full and satisfied even after a large meal, and leading to overeating and purging. Also, a research at the Karolinska Institute in Sweden shows that an imbalance in sex hormones in females can lead to development of Bulimia. These hormonal fluctuations have major role in causing this eating disorder.
Heredity and genetic factor has also been associated with Bulimia. People are more prone to bulimia if they had any family history of bulimia or other eating disorders previously.
Obesity
Obesity can be directly linked with Bulimia. People with bulimia force to vomit in order to eliminate the extra calories they have taken up. Obesity can lead a person to have an altered image of own body, and making him/her try desperately to become thin. This can gradually develop bulimia in the person with the cycle of eating too much, then purging and again eating. Children who have been obese(grossly fat or overweight) since childhood are also more prone to have Bulimia in their adolescence.
Dieting
One of the major misconceptions is that eating less or starving oneself and dieting using Laxatives can effectively help in getting rid of the calories. Bulimia can be caused by strict dieting too. As mentioned previously, starving and eliminating food from body forcefully would only lead to nutritional deficiency. This in turn causes more hunger, then more purging and the whole thing becomes a vicious cycle.
Distressing and traumatic events
People can also have Bulimia after distressing life events such as leaving one’s home, divorce, accidents, loss of a loved one or even during transitions coinciding with puberty. Bulimia is also associated with previous history of sexual abuse and trauma and substance use. Most of them have a low self-esteem after such distressing event, and find food as a means to increase the self- confidence. People with bulimia find food as a medium of comfort and pleasure amidst the tension and stress.
Image Stereotyped Careers
It has been seen that Bulimia can be caused by the extensive pressure put on people from certain career backgrounds such as supermodels, dancers, wrestlers, actors or other sports field. The demand of the job to remain slim and thin can eventually lead to the development of eating disorders like bulimia.
What are the symptoms of Bulimia?
Following are the major symptoms that can be seen in people with bulimia. This is more common in adolescents and people in their late twenties and thirties.
- Having regular and recurrent episodes of binge-eating (eating on an enormous amount of food in a single time) to the extent of feeling sick
- Uncontrolled and rapid eating
- Eating alone most of the times
- Unaware of what, when and how much food is being eaten
- Immediate guilt and distress to have eaten large amount of food
- Forced unhealthy vomiting, or using laxatives (drugs to induce bowel movements) to remove the eaten food immediately, after every meal
- Doing excessive and tough exercises or fasting to get rid of calories
- Scars and signs on the knuckles known as “Russell’s signs”(particularly caused by finger-induced vomiting)
- Swelling in cheeks due to effect on the Parotid glands
- Eyes might have broken blood vessels
- Constantly distressed about weight gain
When To Visit Doctor?
You need to immediately visit a doctor if you’re frequently having the above symptoms for a time period of more than three months. If the eating and purging compulsion have been occurring more than thrice a week, then you should consider consulting a doctor even if it’s less than three months time that you’ve faced these symptoms.
How Is Bulimia Treated?
Bulimia can be treated using a combination of medicines and different therapies.
Medicines
Medicines have been seen as a key component in the treatment process for bulimia. For long lasting relief, anti-depressant medicines are used more commonly in treating this eating disorder. These help to balance certain brain chemicals such as Serotonin (responsible for determining mood of a person) and keep a person’s temperament in control. People using these medicines have seen a reduction in desire to eat and purge within two to four weeks after the intake of medicines.
Cognitive Behavioral therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral therapy is a treatment process in which the therapist has a one to one counseling session with the person having bulimia. The therapist talks with the person, and studies the thinking pattern of the person through different mental exercises. The main aim of CBT is to alter the thoughts and distorted views about body weight, shape, dieting and vomiting to prevent weight gain. The therapist will teach unique ways to control your inner negative thoughts about yourself, and fight with the disorder.
Nutritional counseling
This is another component of the treatment process where you’d learn about the standards of nutritional intakes for a healthy body. The major purpose of nutritional counseling is to aware the person having bulimia about possible health hazards of nutritional deficiency, and how he/she can cope with it. Another objective is to eliminate the belief in the person that vomiting and using laxatives won’t reduce the body weight, but just bring in more health issues.
Family therapy
Family therapy consists of several sessions with families and guardians of the person having bulimia. They are given the knowledge about bulimia, how it is caused and the severity of its consequences. The major aim of family therapy is build support and motivation from family sources during the whole treatment process.
Hospitalization
In rare cases, hospitalization may also be needed during the treatment process. Hospital based treatment is required when the person have critical health conditions due to vigorous vomiting and use of laxatives. It can be severe dehydration, low blood pressure, bleeding in esophagus or stomach or even dangerous heart conditions. The person will be given strict medical care and support to overcome the situation.
Support Groups
There are several support groups for Bulimia in which one will find people with similar stories and problems. He/she can meet other people and get new ideas on how they’re dealing with bulimia. Being in support groups will help to make one feel that he/she is not alone who’s going through this trouble.